- Abiogenesis–the hypothetical process where life spontaneously formed from organic material that had arisen from inorganic material.
- Allele–alternative forms of genes that can have the same place on homologous chromosomes and are responsible for alternative traits.
- Astrobiology–the branch of biology that investigates the existence of living organisms on other planets; similar to Exobiology.
- Australopithecine–supposed human ancestor.
- Cambrian–from 500 million to 600 million years ago; marine invertebrates.
- Chromosome–a threadlike structure in cells that carries genes.
- Cladistics–a system of biological taxonomy based on the quantitative analysis of comparative data which is used to reconstruct trees summarizing the (assumed) phylogenetic relations and evolutionary history of groups of organisms.
- Craniate–animals having a bony or cartilaginous skeleton with a segmented spinal column and a large brain enclosed in a skull or cranium.
- DNA–a nucleic acid consisting of large molecules shaped like a double helix; it is the genetic information and is associated with the transmission of that genetic information.
- Evolution–the theory regarding the sequence of events involved in the evolutionary development of a species or taxonomic group of organisms.
- Exobiology–a branch of biology that examines the possibility of life existing elsewhere in the universe; similar to Astrobiology.
- Extinct–a species of life that is no longer living.
- Fossil–a relic or impression of a plant or animal that existed in a past geological age.
- Gene–a self-replicating protein molecule that resides in a chromosome and is part of the DNA construction.
- Genetic–dealing with genes; a gene is a unit within a chromosome that transmits hereditary characteristics.
- Genetic Drift–the change in frequency in which a gene appears in a population, through mutation, regardless of the adaptive value of the mutation.
- Hominid–any family of two-legged primates, including man.
- Hominoid–a sub-category of primates that includes Humans (Hominids) as well as the great apes (Pongids) and the lesser apes (Hylobates).
- Hypothesis–a tentative explanation for an observation or phenomena that can be tested through experimentation.
- Invertebrate–having no backbone or spinal column.
- Macroevolution–large-scale change in organisms resulting in new species, genera, families, etc.
- Mammal–a warm-blooded, air-breathing vertebrate organism that gives birth to live young that suckle on the milk of their mothers.
- Microevolution–small-scale genetic changes in organisms through mutations resulting in slight changes in an organism.
- Morphology–the branch of biology that deals with the structure of animals and plants.
- Mutation–an organism exhibiting the result of chromosomal alteration.
- Natural selection–the process by which organisms with helpful adaptive qualities are permitted by nature to transmit their genetic information to offspring; it is also the process by which an organism with harmful qualities is removed from the environment.
- Phylogeny–the sequence of events involved in the evolutionary development of a species or taxonomic group of organisms.
- Precambrian–the time before 600 million years ago.
- Primate–any order of animals including man, apes, monkeys, lemurs, etc., characterized by flexible hands and feet.
- Punctuated Equilibrium–the theory that evolution occurs in huge and sudden jumps.
- Science–systemized knowledge derived through experimentation, observation, and study; also, the methodology used to acquire this knowledge.
- Singularities–a unique or peculiar feature or thing.
- Species–a taxonomic group whose members can interbreed.
- Taxonomy— a classification of organisms into groups based on similarities of structure or origin, etc.
- Tetrapod–any vertebrate having four legs or limbs.
- Theory–a statement or set of statements used to explain a phenomenon. A theory is generally accepted as valid due to having survived repeated testing.
- Vertebrate–having a backbone or spinal column.
- Zoology–the branch of science that deals with animal structures, growth, and classification.
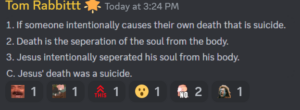
An atheist says that Jesus committed suicide
On the Discord app during the week of 21 November 2023, I had a discussion with an atheist named Tom Rabbittt. I don't...